【罂粟摘要】瑞马唑仑与丙泊酚麻醉在硬质支气管镜检查中苏醒时间的比较:一项前瞻性随机对照试验
瑞马唑仑与丙泊酚麻醉在硬质支气管镜检查中苏醒时间的比较:
一项前瞻性随机对照试验

贵州医科大学 麻醉与心脏电生理课题组
翻 译:安丽 编 辑:柏雪 审 校:曹莹
背景:瑞马唑仑是一种苯二氮卓类新型超短效静脉注射用的镇静催眠药,可显著缩短镇静起效和苏醒时间,并可被氟马西尼拮抗。丙泊酚是硬质支气管镜检查中应用最广的麻醉药,但无特异性拮抗剂,其消除主要由心排量和肝脏代谢。本试验观察在硬质支气管镜下接受气管内手术的患者,应用瑞马唑仑与丙泊酚麻醉后,其苏醒时间的比较。
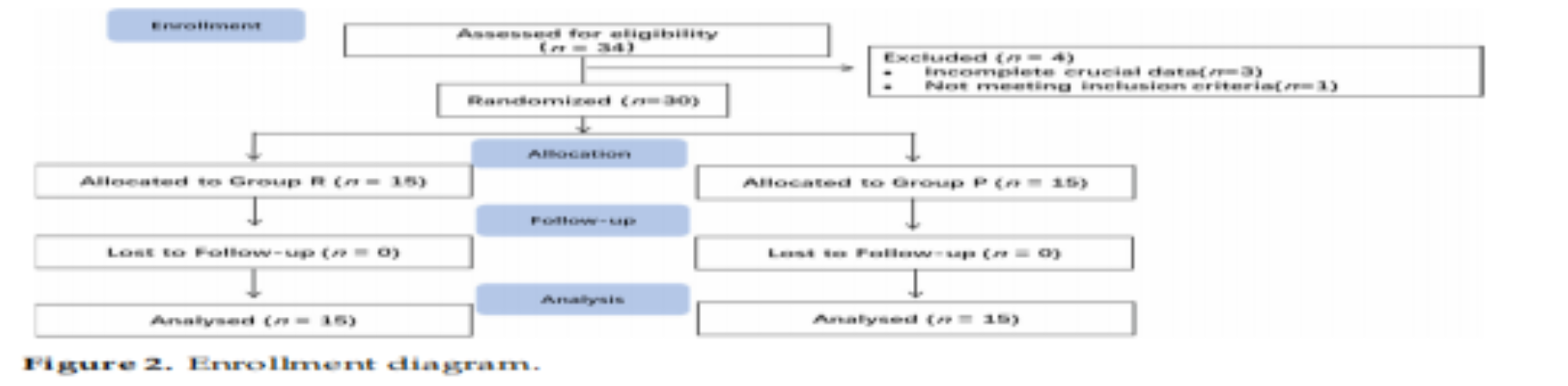
方法:择期行气管内肿瘤切除术或支架置入术的患者,采用随机数字表法分为瑞马唑仑组(R组)和丙泊酚组(P组)。R组:给予0.4 mg/kg瑞马唑仑静脉注射。P组:接受1.5 mg/kg丙泊酚静脉注射。随后两组均使用0.2 mg/kg的羟考酮和0.9 mg/kg的罗库溴铵进行麻醉诱导。诱导后,两组患者均采用高频呼吸机经硬质支气管镜行正压通气,R组给予1 mg/kg/h的瑞马唑仑和6-8µg/kg/h的瑞芬太尼维持。P组患者给予4-8 mg/kg/h的丙泊酚,瑞芬太尼6-8µg/kg/h麻醉维持,维持BIS在40-60,以维持足够的麻醉深度。手术结束时,停止使用镇静药和瑞芬太尼,取出硬质支气管镜后直接将喉罩置入气道。两组均给予2-3 mg/kg Sugammadex 拮抗罗库溴铵。TOF为90%时,R组使用氟马西尼0.5 mg拮抗。符合拔管标准后取出LMA。主要观察指标为麻醉后的苏醒时间。次要观察指标为镇静持续时间(LoC)、术中血流动力学波动和不良事件情况。
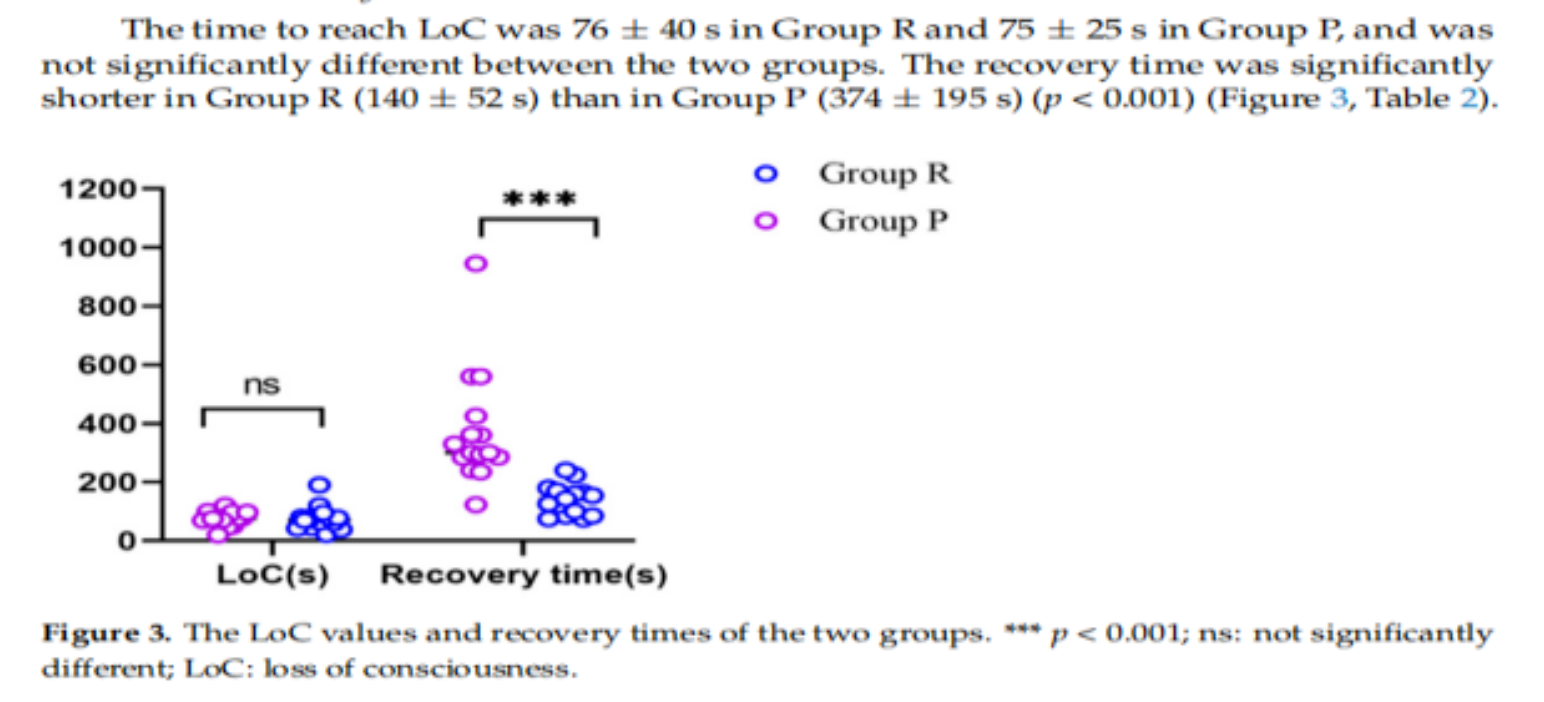
结果:共筛选出34例患者,30例患者纳入研究。R组恢复时间(140±52s)明显短于P组(374±195s) (P<0.001)。LoC时间R组为(76±40s), P组为(75±25s),差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。两组患者在血流动力学波动及不良事件方面差异均无统计学意义。
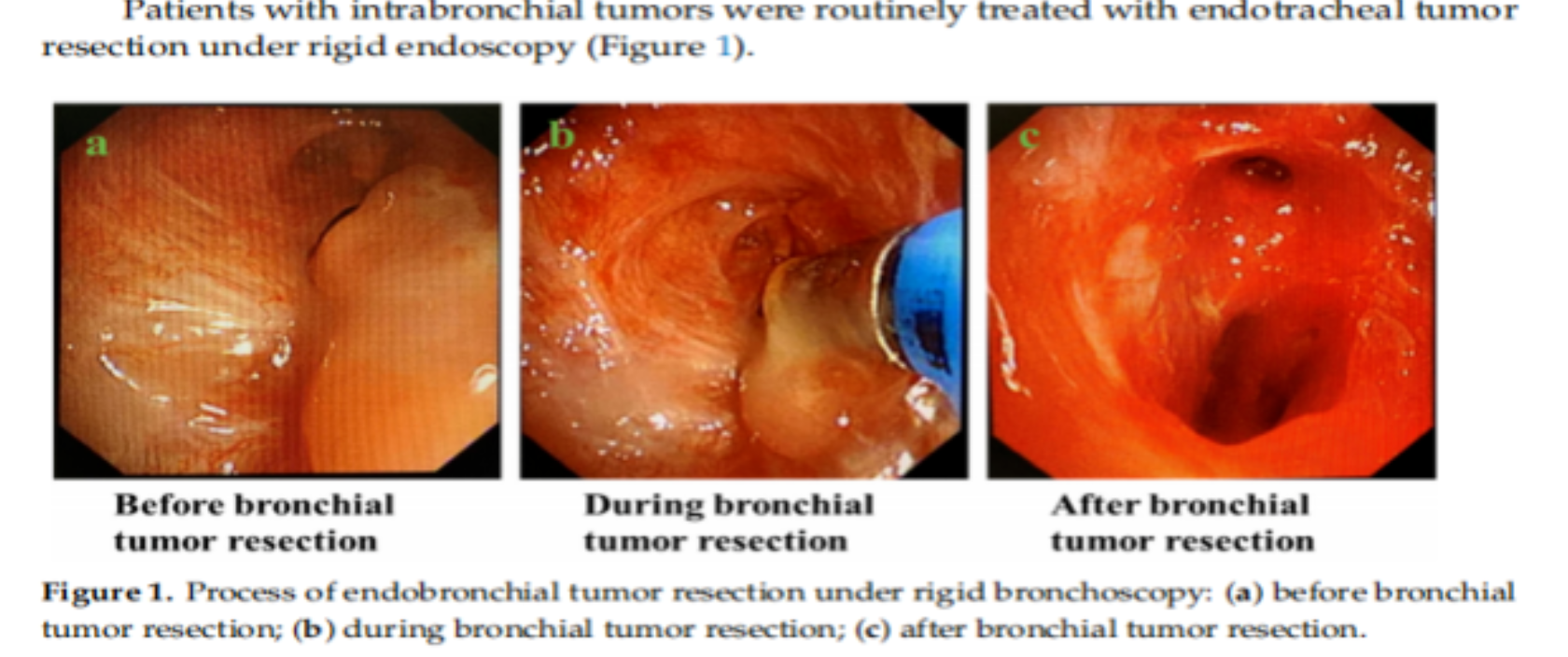
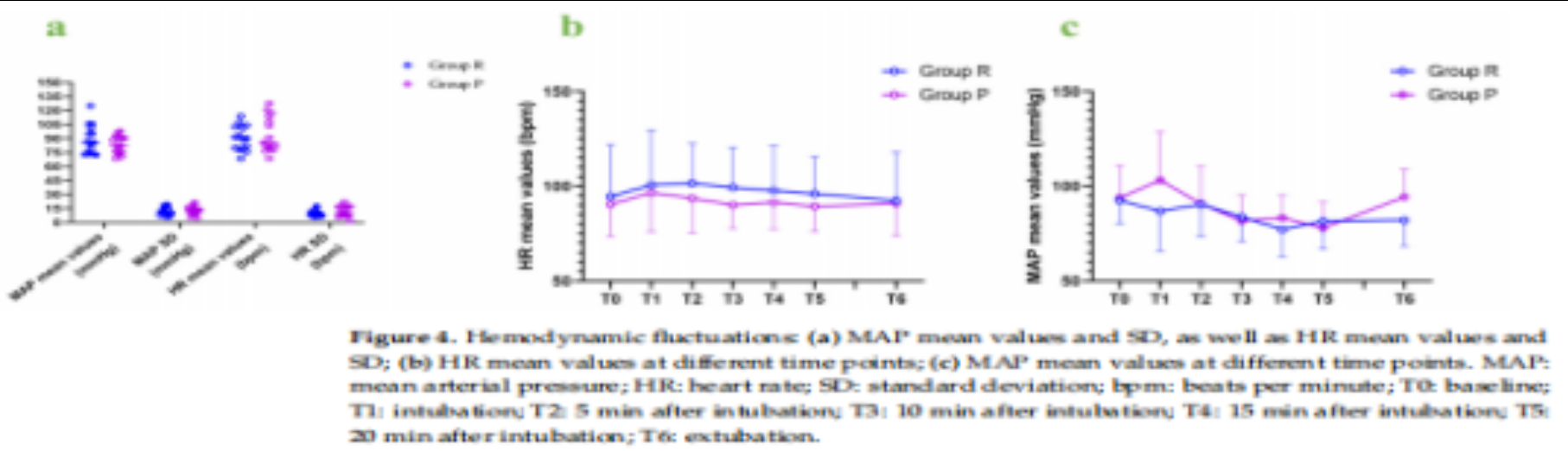
结论:瑞马唑仑用于硬质支气管镜检查患者麻醉后苏醒时间短于丙泊酚,两种药物之间无明显血流动力学波动和不良事件发生的差异。与丙泊酚相比,瑞马唑仑麻醉后可更快的苏醒。
原始文献来源:Yafei Pan , Mo Chen, Fulei Gu , Jinyan Chen , Wen Zhang , Zhangxiang Huang , Dapeng Zhu , Jia Song ,Jun Fang, Weifeng Yu , and Kangjie Xie.Comparison of Remimazolam-Flumazenil versus Propofol for Rigid Bronchoscopy: A Prospective RandomizedControlled Trial.J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12010257.
英文原文:
Comparison of Remimazolam-Flumazenil versus Propofol for
Rigid Bronchoscopy: A Prospective Randomized
Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: Remimazolam is a novel ultrashort-acting intravenous benzodiazepine sedative–hypnotic that significantly reduces the times to sedation onset and recovery. This trial was conducted to confirm the recovery time from anesthesia of remimazolam-flumazenil versus propofol in patients undergoing endotracheal surgery under rigid bronchoscopy.
Methods: Patients undergoing endotracheal tumor resection or stent implantation were randomly allocated into a remimazolam group (Group R) or a propofol group (Group P). The primary outcome was the recovery time from general anesthesia. The secondary outcomes were the time to loss of consciousness (LoC),hemodynamic fluctuations, and adverse events.
Results: A total of 34 patients were screened,and 30 patients were enrolled in the study. The recovery time was significantly shorter for Group R (140 ± 52 s) than for Group P (374 ± 195 s) (p < 0.001). The times to LoC were 76 ± 40 s in Group R and 75 ± 25 s in Group P and were not significantly different. There were also no significant differences in hemodynamic fluctuations or adverse events between the two groups.
Conclusions: The recovery time from general anesthesia in rigid bronchoscopy patients was shorter using remimazolam-flumazenil than with propofol, with no dramatic hemodynamic fluctuations and adverse events or differences between the agents. Remimazolam-flumazenil allows for faster recovery from anesthesia than propofol.
END
来源 | 健康界
版权归原作者所有,若有违规、侵权请联系我们

- 1


